Tutorial 4: Build a zkApp UI in the Browser with React
zkApp programmability is not yet available on the Mina Mainnet. You can get started now by deploying zkApps to the Berkeley Testnet.
In the Hello World tutorial, you built a basic zkApp smart contract with SnarkyJS. You learned to use the zk config command to create a deploy alias in Tutorial 3: Deploy to a Live Network.
In this tutorial, you implement a browser UI using ReactJS that interacts with a smart contract.
Prerequisites
This tutorial has been tested with:
- Mina zkApp CLI version 0.10.0
- SnarkyJS version 0.11.1
- Auro Wallet version 2.2.1
- Ensure your environment meets the Prerequisites for zkApp Developer Tutorials.
- Install the Auro Wallet for Chrome that supports interactions with zkApps. See Install a Wallet and create a MINA account.
Use the working application first
Before you go through the tutorial steps, take a look at a working zkApp UI example that has already been deployed to GitHub Pages.
- In a Chrome web browser with the Auro wallet extension, go to https://es92.github.io/zkApp-examples/index.html.
- When prompted, select Connect to let the website view your Auro wallet account.
- In top middle of the wallet UI, select the Berkeley network:
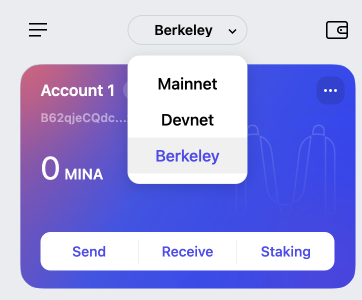
- To look at the console to see what happens when the UI loads SnarkyJS and interacts with the smart contract, right-click the browser window and select Inspect:
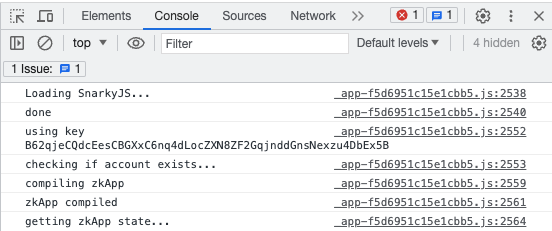
High-Level Overview
In this tutorial, you build an application that:
- Loads a public key from an extension-based wallet.
- Checks if the public key has funds and if not, directs the user to the faucet.
- Connects to the example zkApp
Addsmart contract that is already deployed on Berkeley Testnet at a fixed address. - Implements a button that sends a transaction.
- Implements a button that requests the latest state of the smart contract.
Like previous tutorials, you use the provided example files so you can focus on the React implementation itself.
This example uses an RPC endpoint.
Create a project
The zk project command can scaffold the UI for your project.
Create or change to a directory where you have write privileges.
Create a project by using the
zk projectcommand:$ zk project 04-zkapp-browser-ui --ui nextAt the
? Do you want to setup your project for deployment to Github Pages? …prompt, select yes.When prompted to install the required next packages, press y to proceed.
At the
? Would you like to use TypeScript with this project? › No / Yesprompt, select Yes.At the
? Would you like to use ESLint with this project? › No / Yesprompt, select No.At the
? Would you like to use Tailwind CSS with this project? › No / Yesprompt, select No.
Your UI is created in the project directory: /04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui with two directories:
contracts: The smart contract codeui: Where you write your UI code
For this tutorial, you run commands from the root of the 04-zkapp-browser-ui directory as you work in the ui/src/pages directory on files that contain the UI code.
Each time you make updates, then build or deploy, the TypeScript code is compiled into JavaScript in the build directory.
Preparing the project
Start by deleting the default files that come with the new project.
Change to the
ui/src/pagesdirectory:$ cd ui/src/pagesDelete the old files so that you have a clean project to work with:
$ rm index.page.tsxChange to the
ui/src/stylesdirectory:
$ cd ui/src/styles
Then delete these files:
$ rm globals.css
$ rm Home.module.css
Build the default contract
This tutorial uses the default contract Add that is always scaffolded with the zk project command.
To build the default contract to use in the UI:
$ cd 04-zkapp-browser-ui
$ cd contracts
$ npm run build
If you were to make your own zkApp outside of this tutorial, you edit files in the contracts folder and then rebuild the contract before accessing it from your UI.
Implement the UI
The React UI has a few components: the React page itself and the code that uses SnarkyJS.
Because SnarkyJS code is computationally intensive, it's helpful to use web workers. A web worker handles requests from users to ensure the UI thread isn't blocked during long computations like compiling a smart contract or proving a transaction.
- Download the helper files to your local
/04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui/src/pagesdirectory:
- Review each helper file to understand how they work and how you can extend them for your own zkApp.
zkappWorker.tsis the web worker codezkappWorkerClient.tsis the code that is run from React to interact with the web worker
Add global styles in globals.css
- Copy the files in the
stylesdirectory fromhttps://github.com/o1-labs/docs2/tree/main/examples/zkapps/04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui/stylesto your local/04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui/src/stylesdirectory.
Run the React app
To run the React app, run commands from two different terminal windows in the ui folder.
In the first terminal window:
$ npm run devThis command starts hosting your application at the
localhost:3000default location. Your browser refreshes automatically when your page has changes.And in the second terminal window:
$ npm run ts-watchThis command shows TypeScript errors. As you develop your application, you can watch this window to check for type errors.
Implement the React app
- Copy the
_app.page.tsxfile fromhttps://github.com/o1-labs/docs2/tree/main/examples/zkapps/04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui/src/pagesto your localpagesdirectory.
The import statements just set up your React project with the imports you need. The export statement creates a placeholder empty component:
1 import '../styles/globals.css'
2 import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
3 import './reactCOIServiceWorker';
4
5 import ZkappWorkerClient from './zkappWorkerClient';
6
7 import { PublicKey, Field } from 'snarkyjs';
8
9 let transactionFee = 0.1;
10
11 export default function App() {
12 return <div/>
13 }
14
Add state
This export statement creates mutable state that you can reference in the UI. The state updates as the application runs:
...
11 export default function App() {
12 let [state, setState] = useState({
13 zkappWorkerClient: null as null | ZkappWorkerClient,
14 hasWallet: null as null | boolean,
15 hasBeenSetup: false,
16 accountExists: false,
17 currentNum: null as null | Field,
18 publicKey: null as null | PublicKey,
19 zkappPublicKey: null as null | PublicKey,
20 creatingTransaction: false,
21 });
22
23 // -------------------------------------------------------
24
25 return <div/>
...
To learn more about useState Hooks, see Built-in React Hooks in the React API Reference documentation.
Add a function
This code adds a function to set up the application:
The Boolean
hasBeenSetupensures that the react featureuseEffectis run only once. To learn more aboutuseEffectHooks, see useEffect in the React API Reference documentation.This code also sets up your web worker client that interacts with the web worker running SnarkyJS code to ensure the computationally heavy SnarkyJS code doesn't block the UI thread.
...
23 // -------------------------------------------------------
24 // Do Setup
25
26 useEffect(() => {
27 (async () => {
28 if (!state.hasBeenSetup) {
29 const zkappWorkerClient = new ZkappWorkerClient();
30
31 console.log('Loading SnarkyJS...');
32 await zkappWorkerClient.loadSnarkyJS();
33 console.log('done');
34
35 await zkappWorkerClient.setActiveInstanceToBerkeley();
36
37 // TODO
38 }
39 })();
40 }, []);
41
42 // -------------------------------------------------------
...
Load the zkApp in the web worker
This code loads the contract and compiles it:
...
35 await zkappWorkerClient.setActiveInstanceToBerkeley();
36
37 const mina = (window as any).mina;
38
39 if (mina == null) {
40 setState({ ...state, hasWallet: false });
41 return;
42 }
43
44 const publicKeyBase58: string = (await mina.requestAccounts())[0];
45 const publicKey = PublicKey.fromBase58(publicKeyBase58);
46
47 console.log('using key', publicKey.toBase58());
48
49 console.log('checking if account exists...');
50 const res = await zkappWorkerClient.fetchAccount({
51 publicKey: publicKey!
52 });
53 const accountExists = res.error == null;
54
55 // TODO
56 }
...
Create an instance
This code creates an instance of the contract at a fixed address and gets its current state:
...
53 const accountExists = res.error == null;
54
55 await zkappWorkerClient.loadContract();
56
57 console.log('compiling zkApp');
58 await zkappWorkerClient.compileContract();
59 console.log('zkApp compiled');
60
61 const zkappPublicKey = PublicKey.fromBase58(
62 'B62qiqD8k9fAq94ejkvzaGEV44P1uij6vd6etGLxcR4dA8ZRZsxkwvR'
63 );
64
65 await zkappWorkerClient.initZkappInstance(zkappPublicKey);
66
67 console.log('getting zkApp state...');
68 await zkappWorkerClient.fetchAccount({ publicKey: zkappPublicKey })
69 const currentNum = await zkappWorkerClient.getNum();
70 console.log('current state:', currentNum.toString());
71
72 // TODO
73 }
...
Update the state of the React app
And finally for this function, update the state of the React app:
...
70 console.log('current state:', currentNum.toString());
71
72 setState({
73 ...state,
74 zkappWorkerClient,
75 hasWallet: true,
76 hasBeenSetup: true,
77 publicKey,
78 zkappPublicKey,
79 accountExists,
80 currentNum
81 });
82 }
83 })();
...
Write a new effect
Now that the UI setup is finished, a new effect waits for the account to exist if it didn't exist before.
If the account has been newly created, it must be funded from the faucet.
Later, you add a link in the UI to request funds for new accounts.
...
86 // -------------------------------------------------------
87 // Wait for account to exist, if it didn't
88
89 useEffect(() => {
90 (async () => {
91 if (state.hasBeenSetup && !state.accountExists) {
92 for (;;) {
93 console.log('checking if account exists...');
94 const res = await state.zkappWorkerClient!.fetchAccount({
95 publicKey: state.publicKey!
96 })
97 const accountExists = res.error == null;
98 if (accountExists) {
99 break;
100 }
101 await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
102 }
103 setState({ ...state, accountExists: true });
104 }
105 })();
106 }, [state.hasBeenSetup]);
107
108 // -------------------------------------------------------
...
Create functions for UI buttons
Functions can be triggered when a button is pressed by a user.
First, code for a function that sends a transaction:
...
108 // -------------------------------------------------------
109 // Send a transaction
110
111 const onSendTransaction = async () => {
112 setState({ ...state, creatingTransaction: true });
113 console.log('sending a transaction...');
114
115 await state.zkappWorkerClient!.fetchAccount({
116 publicKey: state.publicKey!
117 });
118
119 await state.zkappWorkerClient!.createUpdateTransaction();
120
121 console.log('creating proof...');
122 await state.zkappWorkerClient!.proveUpdateTransaction();
123
124 console.log('getting Transaction JSON...');
125 const transactionJSON = await state.zkappWorkerClient!.getTransactionJSON()
126
127 console.log('requesting send transaction...');
128 const { hash } = await (window as any).mina.sendTransaction({
129 transaction: transactionJSON,
130 feePayer: {
131 fee: transactionFee,
132 memo: '',
133 },
134 });
135
136 console.log(
137 'See transaction at https://berkeley.minaexplorer.com/transaction/' + hash
138 );
139
140 setState({ ...state, creatingTransaction: false });
141 }
142
143 // -------------------------------------------------------
...
And second, code for a function that gets the latest zkApp state:
...
143 // -------------------------------------------------------
144 // Refresh the current state
145
146 const onRefreshCurrentNum = async () => {
147 console.log('getting zkApp state...');
148 await state.zkappWorkerClient!.fetchAccount({
149 publicKey: state.zkappPublicKey!
150 })
151 const currentNum = await state.zkappWorkerClient!.getNum();
152 console.log('current state:', currentNum.toString());
153
154 setState({ ...state, currentNum });
155 }
156
157 // -------------------------------------------------------...
Update placeholder
Replace the <div/> placeholder with a UI to show the user the state of your application:
...
157 // -------------------------------------------------------
158 // Create UI elements
159
160 let hasWallet;
161 if (state.hasWallet != null && !state.hasWallet) {
162 const auroLink = 'https://www.aurowallet.com/';
163 const auroLinkElem = (
164 <a href={auroLink} target="_blank" rel="noreferrer">
165 {' '}
166 [Link]{' '}
167 </a>
168 );
169 hasWallet = (
170 <div>
171 {' '}
172 Could not find a wallet. Install Auro wallet here: {auroLinkElem}
173 </div>
174 );
175 }
176
177 let setupText = state.hasBeenSetup
178 ? 'SnarkyJS Ready'
179 : 'Setting up SnarkyJS...';
180 let setup = (
181 <div>
182 {' '}
183 {setupText} {hasWallet}
184 </div>
185 );
186
187 let accountDoesNotExist;
188 if (state.hasBeenSetup && !state.accountExists) {
189 const faucetLink =
190 'https://faucet.minaprotocol.com/?address=' + state.publicKey!.toBase58();
191 accountDoesNotExist = (
192 <div>
193 Account does not exist. Please visit the faucet to fund this account
194 <a href={faucetLink} target="_blank" rel="noreferrer">
195 {' '}
196 [Link]{' '}
197 </a>
198 </div>
199 );
200 }
201
202 let mainContent;
203 if (state.hasBeenSetup && state.accountExists) {
204 mainContent = (
205 <div>
206 <button
207 onClick={onSendTransaction}
208 disabled={state.creatingTransaction}
209 >
210 {' '}
211 Send Transaction{' '}
212 </button>
213 <div> Current Number in zkApp: {state.currentNum!.toString()} </div>
214 <button onClick={onRefreshCurrentNum}> Get Latest State </button>
215 </div>
216 );
217 }
218
219 return (
220 <div>
221 {setup}
222 {accountDoesNotExist}
223 {mainContent}
224 </div>
225 );
226 }
The UI has three sections:
setuplets the user know when the zkApp has finished loading.accountDoesNotExistgives the user a link to the faucet if their account hasn't been funded.mainContentshows the current state of the zkApp and buttons to interact with it.The buttons allow the user to create a transaction, or refresh the current state of the application, by triggering the
onSendTransaction()andonRefreshCurrentNum()functions shown in the code.
And that's it! You have reviewed the code for your application.
If you've been using npm run dev, you can now interact with the application on localhost:3000. The application has all of the functionality that is implemented in this tutorial.
Deploying the UI to GitHub Pages
Before you can deploy your project to GitHub Pages, you must push it to a new GitHub repository.
- The GitHub repo must have the same name as the project name.
- In this tutorial, the project name is
04-zkapp-browser-ui. - The
zk projectcommand created the correct project name strings for04-zkapp-browser-uiin thenext.config.jsandpages/reactCOIServiceWorker.tsfiles.
To deploy the UI, run the npm run deploy command in your local /04-zkapp-browser-ui/ui/ directory.
After the script builds your application, uploads it to GitHub, and Github processes it, your application is available at:
https://<username>.github.io/<repo-name>/index.html
Conclusion
Congratulations! You built a React UI for your zkApp. The UI allows users to interact with your smart contract and send transactions to Berkeley Testnet.
You can build a UI for your application using any UI framework, not just React. The zkApp CLI also supports SvelteKit and NuxtJS projects.
You are ready to continue with Tutorial 5: Common Types and Functions to learn about different SnarkyJS types you can use in your application.